Clinical evidence
As a pioneer in the field of liver related elastography, FibroScan® is recognized worldwide as the non-invasive gold standard solution for liver fibrosis and liver steatosis assessment with more than 4,200 peer reviewed publications.

Unique biomarkers for fibrosis and steatosis assessment
Our one-of-a-kind parameters
LSM by VCTE™ (Liver Stiffness Measurement by Vibration-Controlled Transient Elastography), CAP™ (controlled attenuation parameter) and SSM by VCTE™ (Spleen Stiffness Measurement) enable point of care, non-invasive diagnosis and monitoring.
LSM by VCTE™ for liver fibrosis assessment
LSM by VCTE™ is unique, patented and validated for liver fibrosis assessment. It is the standard for non-invasive evaluation of liver stiffness.1
3,800+ peer-reviewed publications support the use of LSM by VCTE™.
CAP™ for liver steatosis assessment
CAP™ is unique, patented and validated for liver steatosis assessment.2,3
1,130+ international and peer-reviewed articles support the use of CAP™.
SSM by VCTE™ for portal hypertension assessment
SSM by VCTE™ is unique, patented and validated for portal hypertension assessment and can be used for risk stratification of patients with advanced chronic liver disease.4
134+peer-reviewed publications support the use of SSM by VCTE™.
The new standard parameters for a better diagnosis and monitoring of chronic liver disease
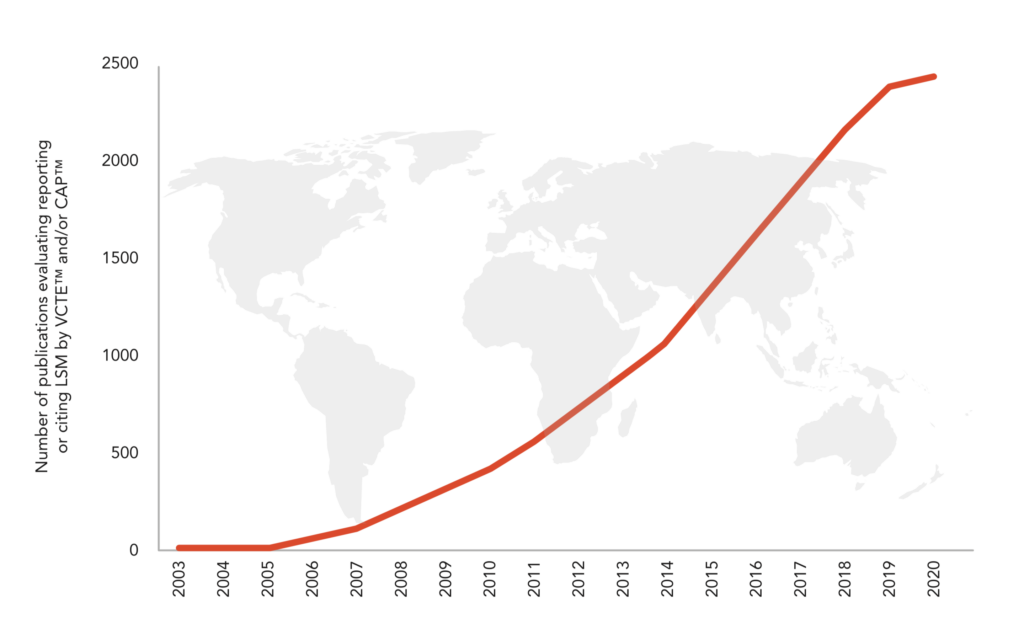
4,200+ peer-reviewed publications and more than 180 international guidelines evaluating, reporting or citing LSM by VCTE™ and CAP™.
VCTE™ can be used to accurately diagnose cirrhosis at an acceptable rate of false negatives and false positives in patients with chronic liver disease.
CAP™ is a point-of-care, standardized and reproducible technique, promising for the detection of liver steatosis.
TE is an established technique and is recommended as the initial assessment for significant liver fibrosis and cirrhosis (A1).
TE is a highly reproducible and user-friendly technique for assessing liver fibrosis in patients with chronic liver disease.
TE can be considered the non-invasive standard for the measurement of liver stiffness.
TE: Most widely used and validated technique for measurement of liver stiffness: standard to be beaten.
Vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE) is the most commonly used imaging-based fibrosis assessment method in the United States.
It has been validated in large cohorts worldwide in a spectrum of liver diseases, including hepatitis B, hepatitis C, fatty liver disease and autoimmune liver disorders, among others.