Application of FIB-4 + LSM by VCTE™ with FibroScan® has Excellent Diagnostic Performance in Screening for Advanced Fibrosis in Diabetology Settings

Study reference
Jachs, et al. Screening for Metabolic Dysfunction–Associated Steatotic Liver Disease–Related Advanced Fibrosis in Diabetology: A Prospective Multicenter Study. Diabates Care, ADA, 2025
| Population type | Patients with MASLD and type 2 diabetes (T2D) or obesity with BMI ≥30kg/m2 |
| Sample Size | 654 patients recruited between 2020 and 2023 |
| Main objective | To assess the feasibility and performance of noninvasive tests (NITs) with that of two-step algorithms for detecting patients at high risk of advanced fibrosis in diabetology and nutrition clinics |
| Acronyms |
T2D: Type 2 Diabetes |
Background & objectives
Patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and obesity are at a significantly higher risk of developing metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) compared to the general population.
Since many individuals with MASLD, especially in its later stages, are asymptomatic, it’s recommended to screen those with T2D and/or obesity, particularly those with other metabolic risk factors.
The consensus is a two-step process: first, calculating the FIB-4 score, and then performing Liver Stiffness Measurement (LSM) using Vibration Controlled Transient Elastography (VCTE™) if the FIB-4 score exceeds 1.3.
The objective of this study was to evaluate and compare the effectiveness and practicality of noninvasive tests (NITs) in identifying patients at high risk of advanced fibrosis, specifically in diabetology and nutrition clinics.
Methods
- 654 patients were included, with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and/or obesity and hepatic steatosis, as determined by conventional ultrasound.
- Liver Stiffness Measurement (LSM) was performed using Vibration Controlled Transient Elastography (VCTE™) along with controlled attenuation parameter (CAP™) on a FibroScan® device, with low and high cutoffs of 8 and 12 kPa, respectively, as per the latest guidelines.
- Liver biopsies were then conducted for patients showing signs of advanced fibrosis after noninvasive screening, with a median interval of 22 weeks between the noninvasive tests and biopsy.
Results
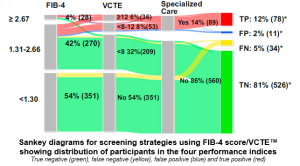
- For risk stratification of advanced fibrosis, 9.3% (n = 61) of participants were identified as having a high risk, 8.3% (n = 54) were at intermediate risk, and consequently, a total of 115 participants (17.6%) required specialized hepatology care.
- For first-line non-invasive test performance, FIB-4 had a higher AUROC at 0.78 compared with NFS at 0.71 and MAF-5 at 0.77. At the low cutoff of <1.30, FIB-4 ruled out the risk of advanced fibrosis in 54.1% of participants, with a high NPV of 97.2% and low false-negative rate of 2.5%. In addition, NFS and MAF-5 ruled out significantly fewer cases (21.9% and 2.7%, respectively).
- The recommended two-step algorithm for referral to hepatology using FIB-4/VCTE™ led to specialized care referral of 12.8–15.4% of participants, including 2% (n = 11) who did not have advanced fibrosis confirmed (see Fig. 1), with a percentage of 81% of true negatives. This support the recommended strategy using a FIB-4 score followed by VCTE™ for MASLD-related fibrosis risk stratification in diabetology settings.
Take home messages
- Effective Screening: A two-step strategy (FIB-4 score followed by VCTE™) effectively identifies patients at high risk of advanced fibrosis.
- Noninvasive Test Performance: FIB-4 outperformed NFS and MAF-5, with a high negative predictive value (97.2%) for ruling out advanced fibrosis.
- Referral to Specialized Care: The FIB-4/VCTE strategy led to appropriate referrals for hepatology care, though 2% of referrals were false positives.
- Practical for Clinics: The two-step approach is practical and effective for identifying high-risk patients in diabetology and nutrition clinics.
The FIB-4 score/VCTE™ algorithm showed excellent diagnostic performance, demonstrating its applicability for routine screening in diabetology.