Fatty liver disease (FLD) is a silent epidemic affecting millions of Americans as the rates of obesity and diabetes continue to accelerate. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its more severe from nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) have a disproportionate impact on minority populations. NAFLD is likely to increase from 83.1 million2 to 100.9 million by 2030, and NASH from 16.52 million to 27 million.
One study2 showed that NAFLD prevalence was highest in Hispanics, intermediate in whites and lowest in blacks. Among patients with NAFLD, risk for progression to NASH was also higher among Hispanics.
FLD Among Hispanic Groups
Studies3 show that Hispanics and patients with diabetes are at greatest risk for both NAFLD and NASH, and the prevalence of both is higher in the Hispanic population. Those with Type 2 diabetes and high rates of liver fat are more likely to have progressive liver disease than those with Type 2 diabetes alone. The 2019 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes issued by the American Diabetes Association recommend that patients with Type 2 diabetes4 or pre-diabetes and elevated liver enzymes or fatty liver on ultrasound should be screened for the presence of liver disease.
Value of Early Detection
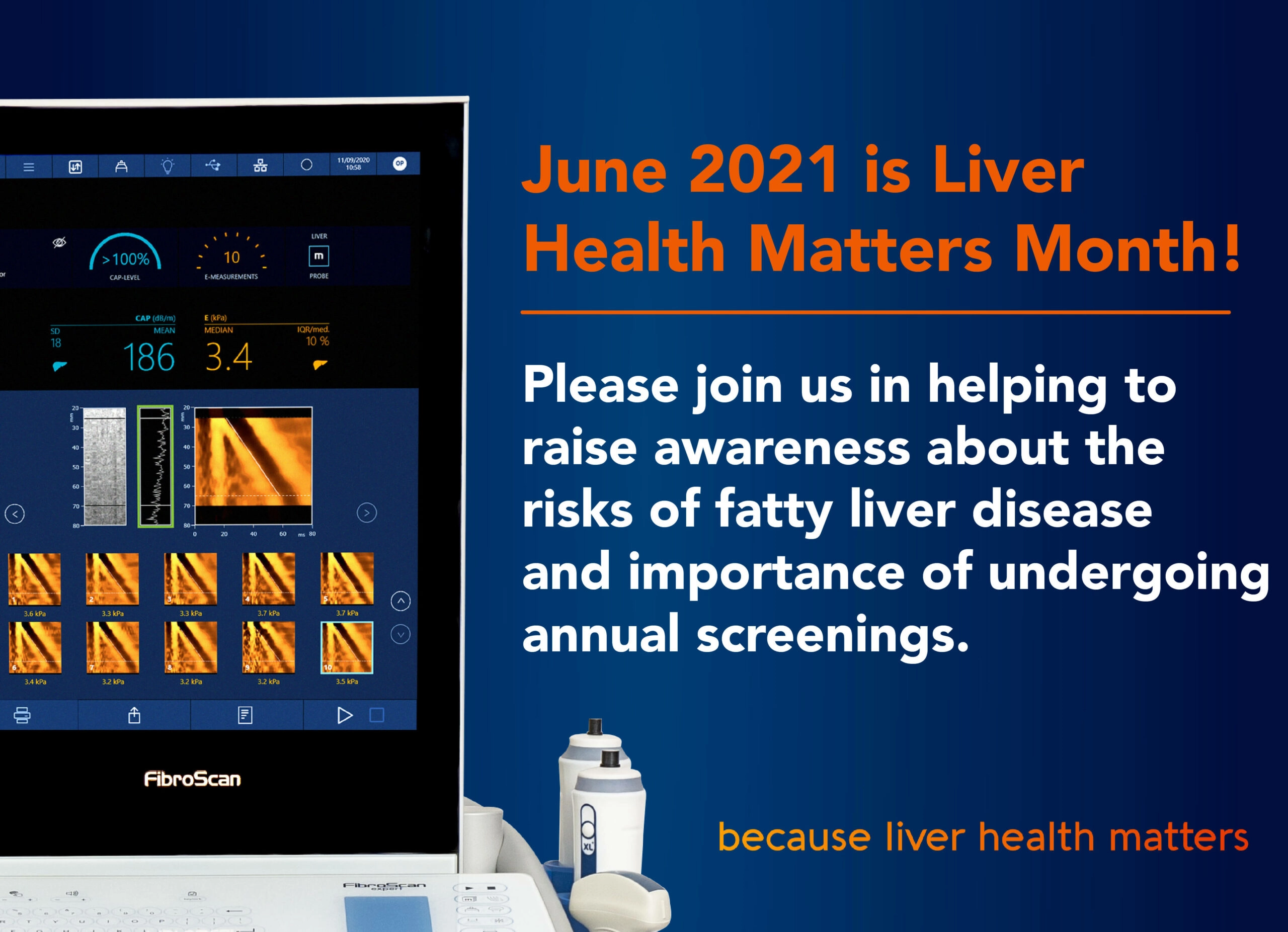
A growing number of physicians are adopting FibroScan®, a rapid, non-invasive technology at the point of care that quickly identifies individuals who are asymptomatic and undiagnosed for liver damage. During National Nutrition Month, we hope more people will spread the message about the dangers of asymptomatic NAFLD/NASH and the importance of early screenings for liver disease among Hispanic populations.
References:
1.National Minority Health Month 2022 website: https://www.minorityhealth.hhs.gov/nmhm/
2. Samji, N.S., Snell, P.D., Singal, A.K. and Satapathy, S.K. (2020), Racial Disparities in Diagnosis and Prognosis of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clinical Liver Disease, 16: 66-72. https://doi.org/10.1002/cld.948
3. Demographics of patients shift as Federally Qualified Health Centers expand| April 20, 2016 | https://healthexec.com/topics/healthcare-policy/demographics-patients-shift-federally-qualified-health-centers-expand
4. American Diabetes Association; 4. Comprehensive Medical Evaluation and Assessment of Comorbidities: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2019. Diabetes Care 1 January 2019; 42 (Supplement_1): S34–S45. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc19-S004