Information for patients
Everything you need to know about liver health
and your liver examination with FibroScan®.

Why is liver health important?
Situated on the right side, in your upper right-hand part of the tummy,
the liver is the largest solid organ in your body and one of the hardest working.
Your liver has 3 main functions
It cleans your blood, it produces an important digestive liquid called bile
and it stores energy in the form of a sugar called glycogen.
There are 3 main causes of chronic liver disease
Metabolic dysfunction associated liver disease (MASLD) and Metabolic associated steatohepatitis (MASH),
Viral hepatitis (HCV and HBV) and Alcohol.
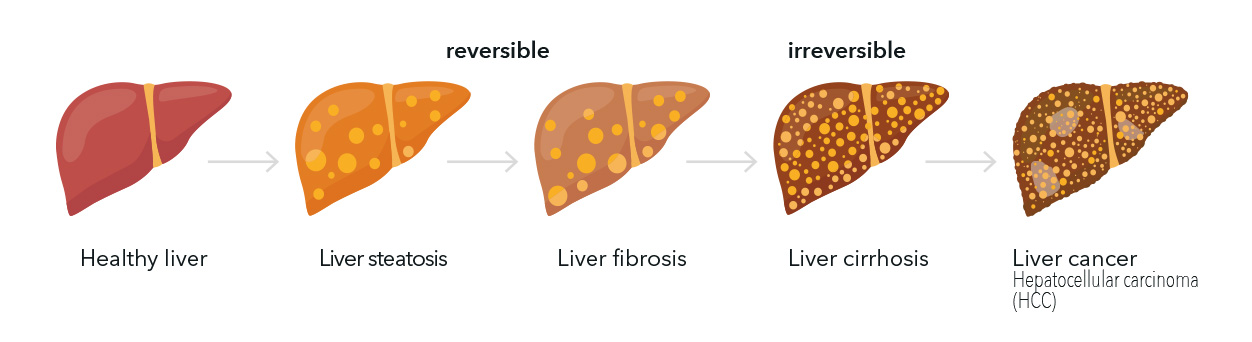
Progression of liver damage
Chronic liver disease is silent and underdiagnosed.
Damage to the liver caused by chronic liver diseases can often be reversed by early diagnosis and intervention.
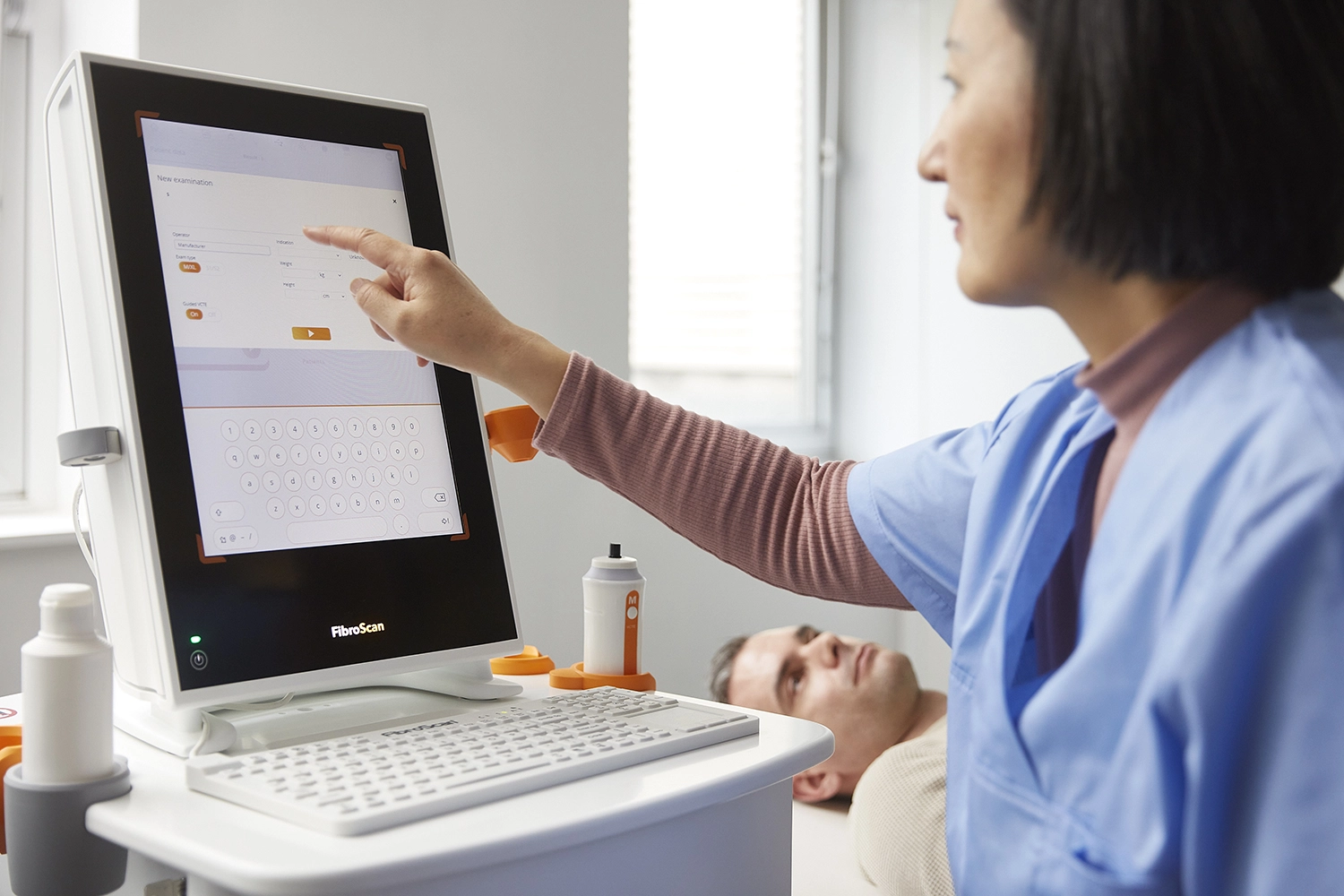
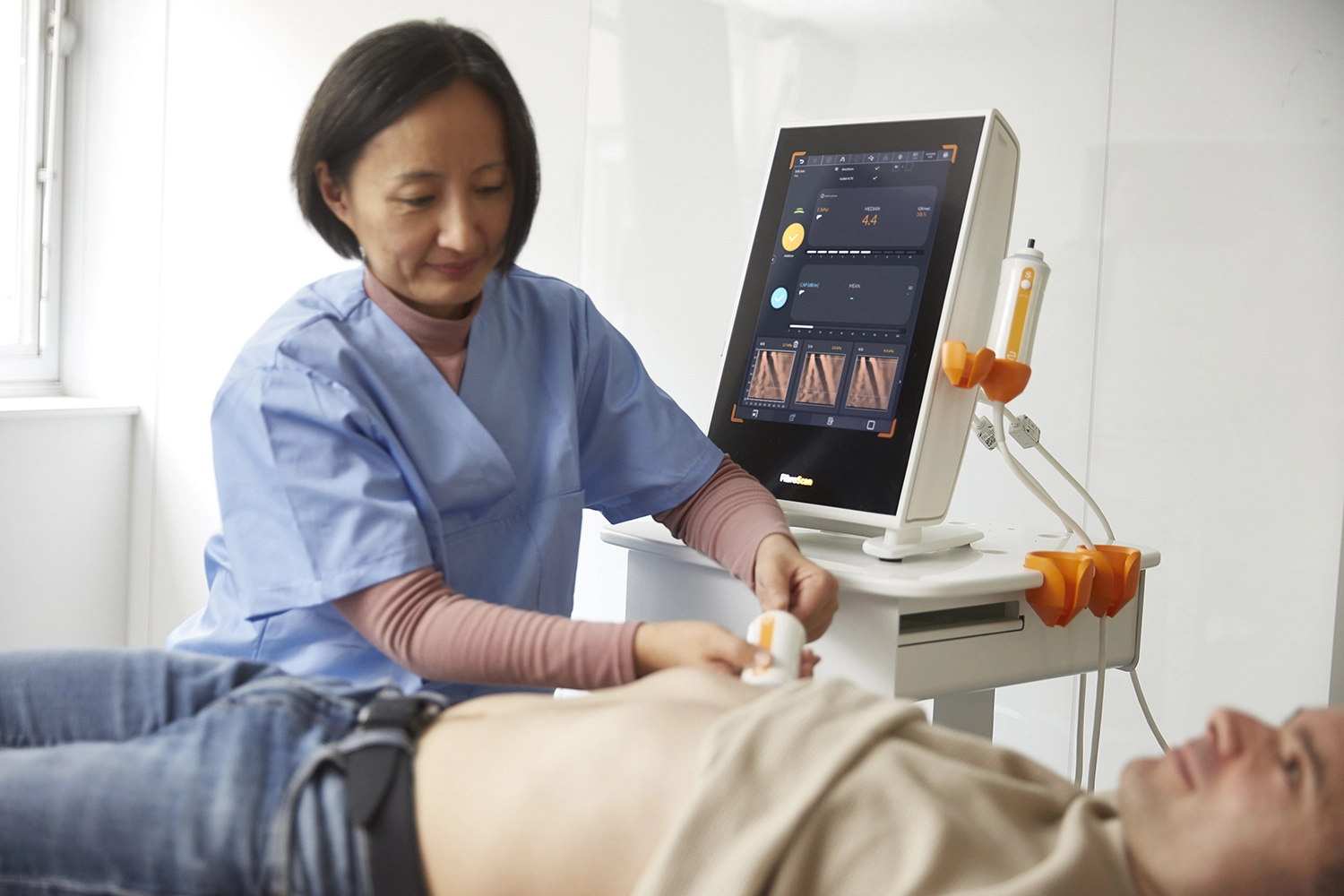
What is FibroScan® ?
FibroScan® is the gold standard non-invasive solution
for comprehensive management of liver health.
It is called non-invasive as nothing enters your body.
FibroScan® sends a pulse of energy to your liver,
which will give your doctor important information about your liver’s health.
Cardiometabolic diseases and implications on liver diseases
Fatty liver is strongly associated with cardiometabolic diseases such as:
prediabetes and type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, hypertension,
insulin resistance, blood lipid disorders, but also sleep apnea,
Polycystic ovary syndrome and hypothyroidism.3,4
Diabetes affects more than 500 million people around the world.5
Almost half of them do not know they have it.
Ignoring this, will put them at an increased risk of complications such as liver disease.
Type 2 diabetes is a risk factor for Metabolic dysfunction associated liver disease (MASLD).
This is the most common chronic liver disease in the world.
If not diagnosed early, it can lead to irreversible damage such as cirrhosis or liver cancer.
1 - Yvonne Huber et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Advanced Liver Fibrosis in a Population-Based Study in Germany, Hepatology Communications, 2022;0:1-10.
2 - Riazi, Kiarash et al. “The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis.” The lancet. Gastroenterology & hepatology vol. 7,9 (2022): 851-861. doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00165-0
3 - European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL). Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A patient guideline. JHEP reports 2021.
4 - Mantovani A. et al. Association Between Primary Hypothyroidism and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Thyroid: Official Journal of the American Thyroid Association 2018, 28 (10): 1270-1284.
5 - International Diabetes Federation website - figures from 2021 - diabetesatlas.org
(76%) - Younossi ZM et al. Hepatology. 2016 Younossi ZM, et al. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease - Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64(1):73-84.9.
(18%) - Kwok R, et al. Gut. 2016. Kwok R, et al. Screening diabetic patients for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with controlled attenuation parameter and liver stiffness measurements: a prospective cohort study. Gut. 2016;65(8):1359-1368.
Recommendations for patients
If you have questions about your FibroScan® results, please speak with your medical care provider.
Discover the new Patient Guide from EASL – European Association for the Study of the Liver – for all patients with or at risk of developing metabolic steatohepatitis (NAFLD).
The purpose of this guide is to support you and help you better understand and manage your disease.