Viral hepatitis
Chronic viral hepatitis is a syndrome characterized by hepatotropic viral infection usually associated with chronic inflammation, hepatocyte injury and progressive fibrosis, that can progress to cirrhosis and associated complications. Hepatitis becomes chronic when infection lasts more than 6 months, typically in the context of HCV or HBV.

Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)
Even if highly efficient antiviral therapies are now available, there are still more than 71 million people worldwide HCV infected patients and approximately 350,000 die each year.12
Improved diagnostic strategies specifically targeting high risk patients are key to halt virus transmission and to achieve elimination by 2030, as a goal set by WHO (World health organization).
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
257 million people were living with chronic hepatitis B infection and 887,000 died of HBV (numbers from 2015).23
Only 10.5% of people living with hepatitis B are aware of their infection, and 16.7% of the diagnosed people are under treatment.23
In this context, prevention of virus transmission, raising awareness among general population, and use of simple diagnostic tests to assess disease stage and eligibility to treatment play a major role to eliminate viral hepatitis B as a health problem.
There are strong correlations of liver stiffness with liver fibrosis in Hepatitis C, Hepatitis B, and also in other causes of liver disease such as MASLD and MASH.
Why screening at-risk patients of viral hepatitis is important?
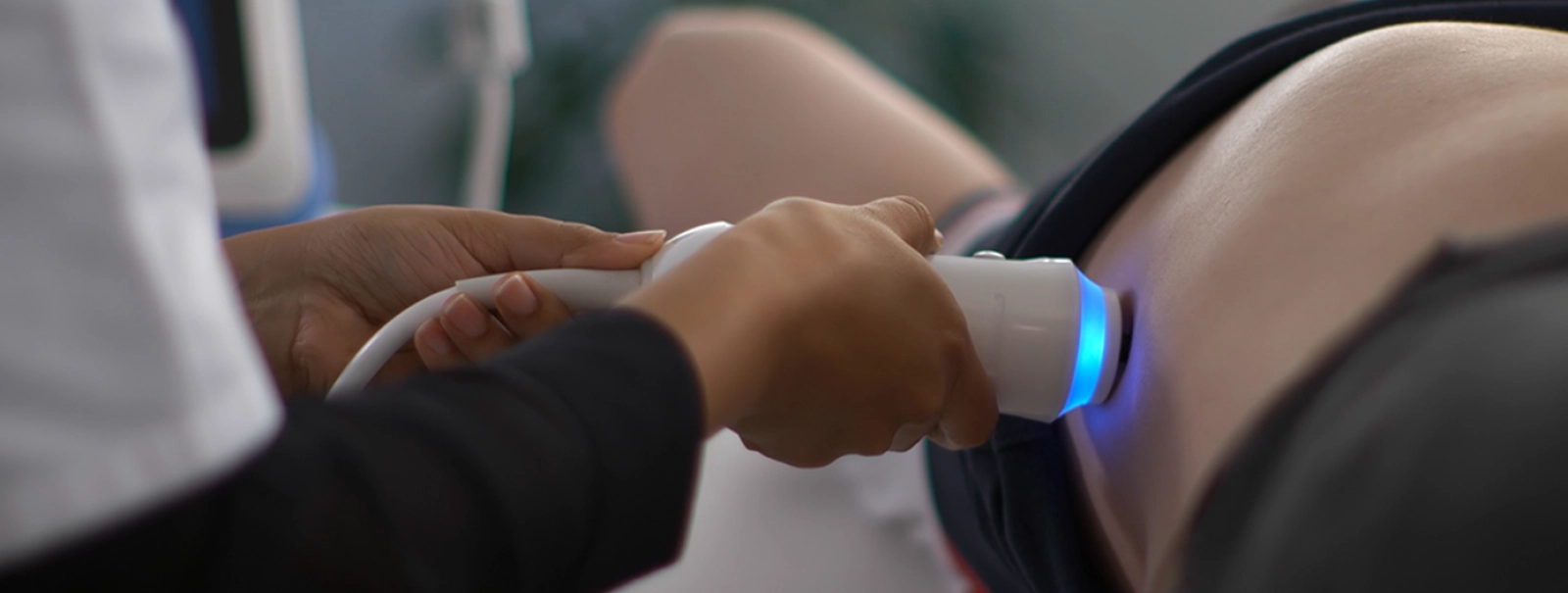
Assessing the degree of fibrosis is a crucial step in the clinical management of persons with viral infection, to detect asymptomatic patients, and also to help prioritize care and to select treatment regimens.
FibroScan® can be used in combination with conventional viral tests, or dry blood spot test for difficult to reach patients, to help identify diseased patients and control the epidemic.
Powered by LSM by VCTE™, FibroScan® benefits from a large clinical validation as a simple, quick and non-invasive diagnostic test for management of patients with chronic viral hepatitis and co-infections, with more than 5 540+ peer–reviewed publications available, and being mentioned in international guidelines.12, 24, 25
Before VCTE™ and CAP™, the only real diagnostic option for assessing patients with hepatitis C virus was biopsy, and even then, we couldn’t always pick up ‘borderline’ cases. We’ve almost stopped doing biopsies now, except in rare diagnostic dilemmas.

References are available in our bibliography.